📌 Key Takeaways
Uncontrolled kraft paper moisture and temperature gradients turn receiving docks into quality failure launch pads—structured conditioning eliminates the guesswork.
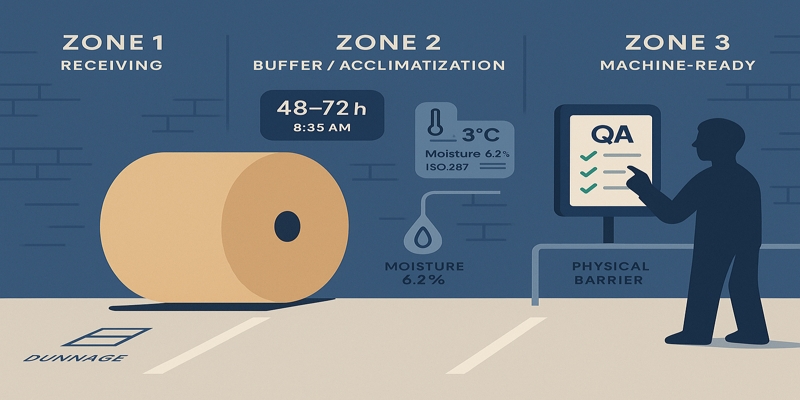
- Three Zones Replace Chaos: Separate receiving, acclimatization, and machine-ready staging with physical barriers and time-in-state tracking to prevent mixing conditioned and unconditioned stock.
- Method-Named Moisture Beats Mill Promises: Transit resets what the supplier’s certificate claimed—document every reading with ISO 287 or TAPPI T 412 codes, timestamps, and tolerances to create audit-ready evidence trails.
- Surface Temperature Confirms Thermal Equilibrium: Infrared measurement within ±3°C of ambient proves the entire reel diameter stabilized, not just the time elapsed since dock arrival.
- The Seven-Point Gate Prevents Line Stops: Release reels only after verifying dock date, time-in-state, surface temperature, moisture evidence, edge condition, wrap integrity, and machine readiness—every checkpoint documented with operator sign-off.
- Curl Signals Process Gaps, Not Bad Luck: When post-conditioning waviness appears despite proper buffer time, extend acclimatization by 24-48 hours, enforce the ±3°C rule without exceptions, and maintain 2-meter clearance from exterior walls.
Prepared = verifiable stability, cleaner runs, and procurement negotiations anchored to data instead of debates.
Kraft paper converting operations managers and quality control supervisors will find a complete implementation framework here, preparing them for the detailed three-zone storage plan, moisture tracking protocols, and pre-run verification checklist that follows.
Quick Answer for Operators: Condition kraft reels in three stages from dock to machine—receive and inspect, buffer to equalize temperature and humidity, then move to machine-ready staging only after confirming stable surface temperature (within ±3°C of ambient), method-named moisture evidence, intact edges, and clean wraps. This sequence reduces curl, dust accumulation, and line stops.

Reel conditioning stabilizes moisture content and temperature gradients in kraft paper before converting operations begin. When executed properly, it reduces curl at unwind, minimizes web breaks, and eliminates quality failures that emerge when operators convert reels straight off the receiving dock without allowing acclimatization.
Consider what happens without conditioning: a reel arrives after weeks in an ocean container where daily temperature swings cause moisture to migrate unpredictably. Operators load this reel immediately, and within minutes curl appears because outer wraps carry different moisture content than inner layers. The resulting line stops, scrap, and rework cost more than the 48-72 hours required for proper stabilization. Reel conditioning becomes an evidence-checked process when aligned to the same ISO and TAPPI test methods mills and QA teams already use—making outcomes verifiable rather than subjective.
From Dock to Stable – The 3-Zone Storage Plan

A structured three-zone approach separates receiving from acclimatization and final staging.
- Zone 1 (Receiving) handles immediate dock inspection for transit damage, edge condition, and wrap integrity—reels pass or move to quarantine within 30 minutes.
- Zone 2 (Buffer/Acclimatization) provides climate-controlled or seasonally managed space where reels stabilize from transit conditions to plant ambient over 48-72 hours minimum, with time-in-state carefully tracked.
- Zone 3 (Machine-Ready) holds conditioned, approved reels adjacent to converting lines where only authorized operators access them.
Physical separation prevents mixing conditioned and unconditioned stock—the leading cause of moisture-related line stops. Floor signage, dedicated dunnage, and QA sign-off gates at zone transitions enforce this discipline. The approach aligns with process capability verification detailed in factory audit for kraft paper manufacturers: a decision checklist.
Moisture – From Lab Number to Floor Reality

Transit alters moisture content unpredictably. A supplier certificate showing 7% moisture at the mill means little after the reel experiences container condensation cycles during ocean shipping. Conditioning logs must capture this reality by recording the supplier’s lab result (with test method code and date), then adding timestamped entries at dock receipt and post-acclimatization. ISO 287¹ and TAPPI T 412² provide standardized oven-drying methods that enable valid comparisons across these measurement points.
Document moisture readings using the method name beside the value—for example, “Moisture 6.2%, ISO 287” or “Moisture 5.8%, TAPPI T 412″—to create audit-ready evidence trails that both QA teams and suppliers recognize. Moisture drift of 1-2% during transit is normal and manageable through proper acclimatization; larger deviations trigger supplier discussions and potential rejection. For RFQ-stage specification guidance, TAPPI/ISO in plain english: which test methods to require provides ready-to-copy language for moisture test requirements.
The 7 Checks Before You Cut the Reel
This final quality gate within the Machine Compatibility Checklist (Reel & Core Fit) determines whether conditioning succeeded or exposed process gaps:
- Dock date: Confirm minimum conditioning window elapsed (48-72 hours standard, extended for heavyweight grades or extreme climate differentials)
- Time-in-state: Verify reel spent required duration in the buffer zone specifically, not just total site time since arrival
- Surface temperature: Infrared measurement within ±3°C of ambient confirms thermal equilibrium across the reel diameter
- Moisture evidence: Post-conditioning test showing method name, timestamp, and result within RFQ tolerance (for example, “Moisture 6.0%, ISO 287”)
- Edge condition: Visual inspection rejecting damage extending >5mm inward or affecting >10% of circumference
- Wrap integrity: No tears or punctures that allowed moisture ingress during transit or storage
- Machine readiness: Correct grade settings loaded, tension profiles configured, Reel & Core Fit dimensions verified, and pre-run dust control completed
For broader quality specification context, see kraft paper RFQ fields that change the quote.
Handling & Stacking to Prevent Edge Damage and Dust
Keep reels off the floor, protect edges during movement, and control dust before each run. Use appropriate lift truck attachments or padded slings designed specifically for rolls³—avoid bare forks against paper edges, as even minor crushing compromises web stability. Training operators on proper attachment use and regular inspection protocols form part of good handling practice⁴.
Stack only within the reel and core limits specified in supplier documentation. Maintain aisle spacing for airflow and safe access, typically 0.5 meters minimum between rows. Keep protective wraps intact until staging at the machine, then implement pre-run dust control at unwind and nip points using compressed air or soft brushes in a designated containment area.
Troubleshooting Curl & Waviness After Conditioning

When curl appears despite proper conditioning time, three causes dominate.
- Residual moisture gradient between core and outer wraps creates differential expansion at unwind as paper seeks equilibrium with ambient conditions—extend conditioning by 24-48 hours and consider core-out unwinding for heavyweight grades.
- Premature zone transfer means surface temperature matched ambient but internal layers remained thermally unequal; enforce the ±3°C surface check with no exceptions, returning any marginal reels to the buffer zone.
- Storage near exterior walls or uninsulated doors subjects one reel side to outdoor humidity cycling while the opposite side stabilizes, producing directional curl that tension adjustments cannot correct—maintain 2-meter minimum clearance from building perimeter.
Pause production when post-conditioning curl emerges rather than attempting to “run through it.” The relationship between specification tolerances and operating costs is detailed in quality specs vs price: how specs shape real cost.
Supplier Collaboration – Ask for Evidence, Not Assurances
Conditioning programs succeed or fail based on incoming material quality. Request specific documentation at quote and pre-shipment stages: moisture certificates stating ISO 287 or TAPPI T 412 with test dates within 14 days of production and results inside RFQ-specified ranges; packing notes documenting wrap materials, wrapping procedures, and mill storage duration before shipment; transit advisories for grades shipping from extreme climates that require extended acclimatization periods.
When supplier evidence consistently aligns with incoming QC results, the partnership proves reliable. When discrepancies appear, documentation supports corrective action or supplier changes. To identify manufacturers demonstrating process transparency, browse kraft paper manufacturers or kraft paper suppliers who understand method-named evidence requirements.
Frequently Asked Questions
How long should kraft reels acclimatize before converting?
Time depends on transit conditions, reel diameter, basis weight, and seasonal factors rather than a single universal standard. Use the three-zone plan and release reels only when surface temperature and method-named moisture checks indicate stability—typically 48-72 hours minimum, with extensions for heavyweight grades or extreme climate differentials.
What warehouse RH and temperature practices reduce kraft curl?
Stable conditions matter more than any single “ideal” setpoint. Avoid large swings and stratified zones by keeping reels away from exterior walls, loading docks, and HVAC discharge that create moisture and temperature gradients. Climate-controlled buffer zones work best, but seasonally managed spaces with consistent ambient conditions also prove effective.
How do I document reel conditioning so QA and suppliers accept it?
Use timestamped entries that name the test method beside any moisture value—for example, “Moisture 6.2%, ISO 287, 2025-10-24, 14:30, Operator JM.” Keep receiving and pre-run entries together with work orders, linking supplier certificates to your incoming inspection results for complete traceability.
Why does waviness return after transit and how do I fix it?
Transit resets temperature and moisture gradients as containers experience daily cycling between hot and cold conditions. Reels may need additional buffer time beyond standard minimums to reach equilibrium before cutting—extend by 24-48 hours when waviness appears and verify moisture readings stabilize within tolerance before releasing to production.
Structured conditioning transforms receiving docks from logistics bottlenecks into quality control gates. The three-zone storage plan, moisture tracking aligned to ISO/TAPPI standards, and the seven-point pre-run checklist create systems where curl and waviness become manageable exceptions rather than daily disruptions. This approach requires floor space for zoning, infrared thermometers, moisture testing equipment, and operator training—but returns immediate benefits through reduced line stops, lower scrap rates, and procurement negotiations anchored to verifiable data. The Machine Compatibility Checklist (Reel & Core Fit) extends beyond physical dimensions to encompass complete material readiness for converting operations.
Ready to find suppliers who understand conditioning requirements?
→ Browse Kraft Paper Suppliers
→ Browse Kraft Paper Manufacturers
Disclaimer
This article provides general information about reel storage and conditioning for kraft paper for educational purposes. Individual circumstances vary significantly based on factors like facility layout, ambient climate/seasonality, material construction (basis weight/plies), and handling equipment & safety procedures. For personalized guidance tailored to plant-specific run-readiness needs, consult your mill’s technical documentation and a qualified safety professional.
References & External Resources
- ISO 287 – Paper and board — Determination of moisture content — Oven-drying method. International Organization for Standardization. Referenced alongside ISO 638 series for paper testing standards.
- TAPPI T 412 om-22 – Moisture in Pulp, Paper and Paperboard. Technical Association of the Pulp and Paper Industry.
- OSHA eTool for Powered Industrial Trucks – Operator training and safe use of roll clamps and attachments. Occupational Safety and Health Administration.
- OSHA Materials Handling and Storage – General guidance for safe reel movement and storage area design. Occupational Safety and Health Administration.
Our Editorial Process
Our expert team uses AI tools to help organize and structure our initial drafts. Every piece is then extensively rewritten, fact-checked, and enriched with first-hand insights and experiences by expert humans on our Insights Team to ensure accuracy and clarity.
About the PaperIndex Insights Team
The PaperIndex Insights Team is our dedicated engine for synthesizing complex topics into clear, helpful guides. While our content is thoroughly reviewed for clarity and accuracy, it is for informational purposes and should not replace professional advice.